While Android supports most Java language features, it doesn’t support every API that Java provides. On the other hand, Kotlin multiplatform only allows sharing code across all targets (commonMain), not a subset of targets (commonJvm).
Read on to learn how to share part of your code between Android and Java (Jvm), while still providing platform-specific implementations of some classes.
Problem description#
In a typical Kotlin multiplatform project, there is a commonMain SourceSet (blue) which defines both common code and expected code for specific SourceSets (orange):
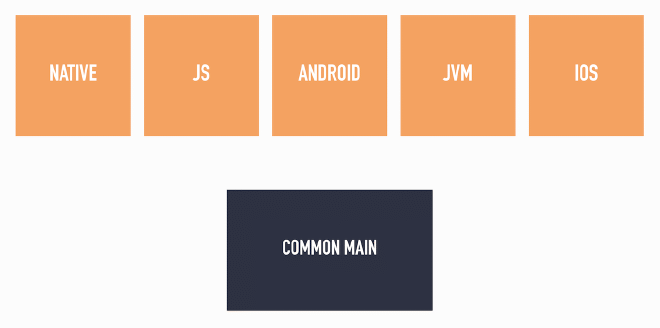
Besides making use of the common code, the specific SourceSets also must provide actual implementations for the expected code.
While this mechanism works great, it doesn’t allow to share code between specific SourceSets. Take for instance Android and Jvm, they have a lot of common API’s but some (e.g. Base64) are different.
As such Android has defined its own android.util.Base64 class which is different from the Jvm java.util.Base64 class. (Though API level 26 and higher also support java.util.Base64)
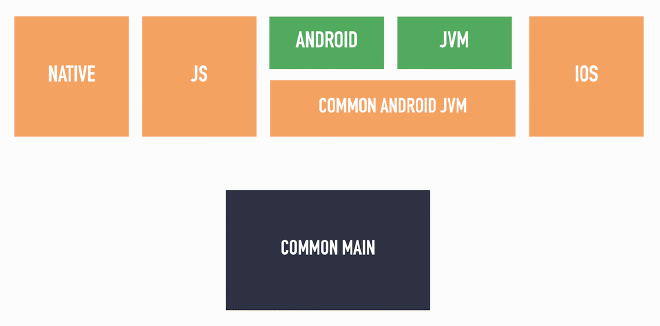
So the challenge at hand is to share most actual implementations across Android and Jvm, but provide platform-specific implementations for some functions.
Visually speaking we would like to accomplish the following:
Approach 1: New sourceset#
Inspired by an example from Sergey Igushkin, let’s add a new sourceSet commonJvmAndroid that will have the shared actual implementations across Android and Jvm.
This requires the following:
- create a new folder
commonJvmAndroidundersrc - create a new
SourceSetcalledcommonJvmAndroid - make
androidMainandjvmMaindepend on this newSourceSet
And the resulting build.gradle.kts file will be:
kotlin {
...
sourceSets {
...
// Must be defined before androidMain and jvmMain
val commonJvmAndroid = create("commonJvmAndroid") {
dependsOn(commonMain)
}
val androidMain by getting {
dependsOn(commonJvmAndroid)
dependencies {
...
}
}
val jvmMain by getting {
dependsOn(commonJvmAndroid)
dependencies {
...
}
}
}
}
While this solution works great from the command line, Intellij autocomplete unfortunately doesn’t work and all Java imports show up red.
I suspect this is because Intellij doesn’t know what kind of SourceSet commonJvmAndroid is, whereas it can recognize the default multiplatform SourceSets.
Approach 2: New srcDir#
To ensure Intellij autocomplete works, a srcDir can be added to the existing SourceSets.
- create a new folder
commonJvmAndroidundersrc - add this new sourceSet to
androidMainandjvmMain
And the resulting build.gradle.kts file will be:
kotlin {
...
sourceSets {
...
val androidMain by getting {
kotlin.srcDir("src/commonJvmAndroid/kotlin")
dependencies {
...
}
}
val jvmMain by getting {
kotlin.srcDir("src/commonJvmAndroid/kotlin")
dependencies {
...
}
}
}
}
Because there is no new sourceSet, Intellij will implicitly use the Android or Jvm one while browsing code in commonAndroidJvm, and hence autocomplete will work!
Real-life example#
Want a bigger example of this principle in action? Have a look at the awesome PbandK project, that provides a Kotlin code generator and runtime for Protocol Buffers. It is built to work across multiple Kotlin platforms.
In the runtime module, the build.gradle.kts adds the extra srcDir to androidMain/jvmMain and the src directory has the shared code in a commonAndroidJvm folder.
Wrap-up#
While Android and Jvm projects share most APIs, not every Java API is available on Android. To share a subset of code across both platforms, it’s best to use a shared srcDir so Intellij autocomplete works as expected.
If you’ve made it this far you should probably follow me on Mastodon. Feel free to leave a comment below!
